Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Predicting with different quantile interpolation methods#
An example comparison of interpolation methods that can be applied during prediction when the desired quantile lies between two data points.
This example was heavily inspired by quantile-forest package. See their package here.
from collections import defaultdict
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
Generate the data#
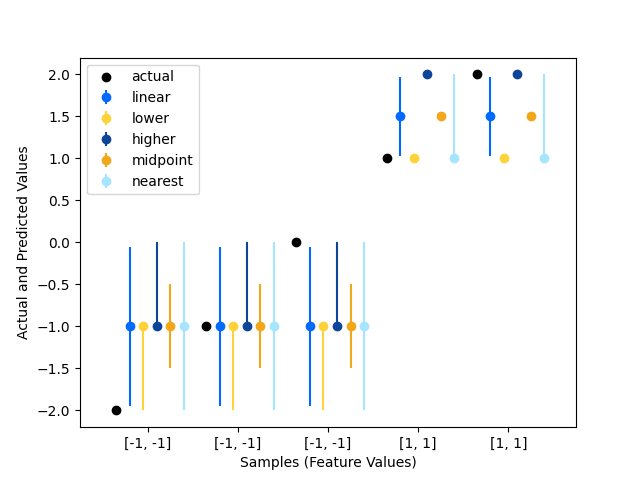
We use four simple data points to illustrate the difference between the intervals that are generated using different interpolation methods.
The interpolation methods#
The following interpolation methods demonstrated here are:
To interpolate between the data points, i and j (i <= j),
linear, lower, higher, midpoint, or nearest. For more details, see treeple.RandomForestRegressor.
The difference between the methods can be illustrated with the following example:
interpolations = ["linear", "lower", "higher", "midpoint", "nearest"]
colors = ["#006aff", "#ffd237", "#0d4599", "#f2a619", "#a6e5ff"]
quantiles = [0.025, 0.5, 0.975]
y_medians = []
y_errs = []
est = RandomForestRegressor(
n_estimators=1,
random_state=0,
)
# fit the model
est.fit(X, y)
# get the leaf nodes that each sample fell into
leaf_ids = est.apply(X)
# create a list of dictionary that maps node to samples that fell into it
# for each tree
node_to_indices = []
for tree in range(leaf_ids.shape[1]):
d = defaultdict(list)
for id, leaf in enumerate(leaf_ids[:, tree]):
d[leaf].append(id)
node_to_indices.append(d)
# drop the X_test to the trained tree and
# get the indices of leaf nodes that fall into it
leaf_ids_test = est.apply(X)
# for each samples, collect the indices of the samples that fell into
# the same leaf node for each tree
y_pred_quantile = []
for sample in range(leaf_ids_test.shape[0]):
li = [
node_to_indices[tree][leaf_ids_test[sample][tree]] for tree in range(leaf_ids_test.shape[1])
]
# merge the list of indices into one
idx = [item for sublist in li for item in sublist]
# get the y_train for each corresponding id``
y_pred_quantile.append(y[idx])
for interpolation in interpolations:
# get the quatile preditions for each predicted sample
y_pred = [
np.array(
[
np.quantile(y_pred_quantile[i], quantile, method=interpolation)
for i in range(len(y_pred_quantile))
]
)
for quantile in quantiles
]
y_medians.append(y_pred[1])
y_errs.append(
np.concatenate(
(
[y_pred[1] - y_pred[0]],
[y_pred[2] - y_pred[1]],
),
axis=0,
)
)
sc = plt.scatter(np.arange(len(y)) - 0.35, y, color="k", zorder=10)
ebs = []
for i, (median, y_err) in enumerate(zip(y_medians, y_errs)):
ebs.append(
plt.errorbar(
np.arange(len(y)) + (0.15 * (i + 1)) - 0.35,
median,
yerr=y_err,
color=colors[i],
ecolor=colors[i],
fmt="o",
)
)
plt.xlim([-0.75, len(y) - 0.25])
plt.xticks(np.arange(len(y)), X.tolist())
plt.xlabel("Samples (Feature Values)")
plt.ylabel("Actual and Predicted Values")
plt.legend([sc] + ebs, ["actual"] + interpolations, loc=2)
plt.show()
Estimated memory usage: 224 MB