Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Speed of Extra Oblique Random Forest vs Oblique Random Forest on different dataset sizes#
A performance comparison between extra oblique forest and standard oblique random forest on different dataset sizes. The purpose of this comparison is to show the speed of changes for each models as dataset size increases. For more information, see [1].
The datasets used in this example are from the OpenML benchmarking suite are:
[Phishing Website](https://www.openml.org/search?type=data&sort=runs&id=4534)
[har](https://www.openml.org/search?type=data&sort=runs&id=1478)
dataset |
samples |
features |
datatype |
Phishing Website |
11055 |
30 |
nominal |
har |
10299 |
562 |
numeric |
Note
In the following example, the parameters max_depth and ‘max_features` are
set deliberately low in order to pass the CI test suit. For normal usage, these parameters
should be set to appropriate values depending on the dataset.
Discussion#
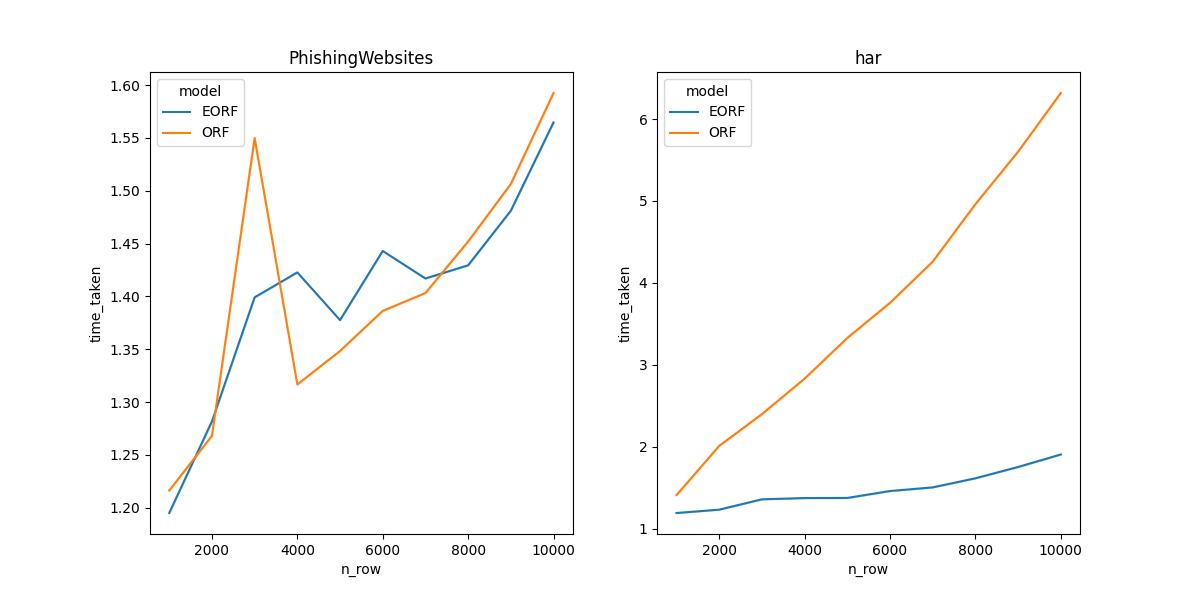
In this section, the focus is on the time taken to train each model. The results show that extra oblique random forest is faster than standard oblique random forest on all datasets. Notably, the speed of extra oblique random forest and oblique random forest grows linearly with the increase in sample size but grows faster for the oblique random forest. The difference between the two models is more significant on datasets with higher dimensions.
References#
from datetime import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedKFold, cross_validate
from treeple import ExtraObliqueRandomForestClassifier, ObliqueRandomForestClassifier
# Model Parameters
max_depth = 3
max_features = "sqrt"
max_sample_size = 10000
random_state = 123
n_estimators = 50
# Datasets
phishing_website = 4534
har = 1478
data_ids = [phishing_website, har]
df = pd.DataFrame()
def load_cc18(data_id, sample_size):
df = fetch_openml(data_id=data_id, as_frame=True, parser="pandas")
# extract the dataset name
d_name = df.details["name"]
# Subsampling large datasets
n = sample_size
if n > max_sample_size:
n = max_sample_size
df = df.frame.sample(n, random_state=random_state)
X, y = df.iloc[:, :-1], df.iloc[:, -1]
return X, y, d_name
def get_scores(X, y, d_name, n_cv=5, n_repeats=1, **kwargs):
clfs = [ExtraObliqueRandomForestClassifier(**kwargs), ObliqueRandomForestClassifier(**kwargs)]
dim = X.shape
tmp = []
for i, clf in enumerate(clfs):
t0 = datetime.now()
cv = RepeatedKFold(n_splits=n_cv, n_repeats=n_repeats, random_state=kwargs["random_state"])
test_score = cross_validate(estimator=clf, X=X, y=y, cv=cv, scoring="accuracy")
time_taken = datetime.now() - t0
# convert the time taken to seconds
time_taken = time_taken.total_seconds()
tmp.append(
[
d_name,
dim,
["EORF", "ORF"][i],
test_score["test_score"],
test_score["test_score"].mean(),
time_taken,
]
)
df = pd.DataFrame(tmp, columns=["dataset", "dimension", "model", "score", "mean", "time_taken"])
df = df.explode("score")
df["score"] = df["score"].astype(float)
df.reset_index(inplace=True, drop=True)
return df
params = {
"max_features": max_features,
"n_estimators": n_estimators,
"max_depth": max_depth,
"random_state": random_state,
"n_cv": 10,
"n_repeats": 1,
"n_jobs": -1,
}
for data_id in data_ids:
for n in np.linspace(1000, max_sample_size, 10).astype(int):
X, y, d_name = load_cc18(data_id=data_id, sample_size=n)
tmp = get_scores(X=X, y=y, d_name=d_name, **params)
df = pd.concat([df, tmp])
df["n_row"] = [item[0] for item in df.dimension]
# Show the time taken to train each model
df_tmp = df.groupby(["dataset", "n_row", "model"])[["time_taken"]].mean()
# Draw a comparison plot
d_names = df.dataset.unique()
N = d_names.shape[0]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, N)
# plot the results with time taken on y axis and sample size on x axis
fig.set_size_inches(6 * N, 6)
for i, d_name in enumerate(d_names):
df_tmp = df[df["dataset"] == d_name]
sns.lineplot(data=df_tmp, x="n_row", y="time_taken", hue="model", color="dataset", ax=ax[i])
ax[i].set_title(d_name)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 40.246 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 456 MB