Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Calculating CMI#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from scipy.stats import entropy
from sktree.datasets import make_trunk_classification
from sktree.ensemble import HonestForestClassifier
from sktree.stats import build_oob_forest
from sktree.tree import MultiViewDecisionTreeClassifier
sns.set(color_codes=True, style="white", context="talk", font_scale=1.5)
PALETTE = sns.color_palette("Set1")
sns.set_palette(PALETTE[1:5] + PALETTE[6:], n_colors=9)
sns.set_style("white", {"axes.edgecolor": "#dddddd"})
CMI#
Conditional mutual information (CMI) measures the dependence of Y on
X conditioned on Z. It can be calculated by the difference between
the joint MI (I([X, Z]; Y)) and the MI on Z (I(Y; Z)):
\[I(X; Y | Z) = I([X, Z]; Y) - I(Y; Z)\]
With a multiview binary class simulation as an example, this tutorial
will show how to use treeple to calculate the statistic with
multiview data.
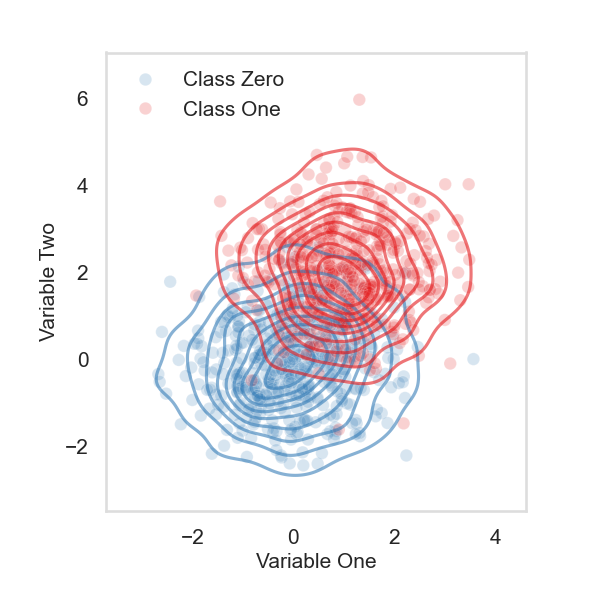
Create a simulation with two gaussians#
# create a binary class simulation with two gaussians
# 500 samples for each class, class zero is standard
# gaussian, and class one has a mean at one for Z
Z, y = make_trunk_classification(
n_samples=1000,
n_dim=1,
mu_0=0,
mu_1=1,
n_informative=1,
seed=1,
)
# class one has a mean at two for X
X, y = make_trunk_classification(
n_samples=1000,
n_dim=1,
mu_0=0,
mu_1=2,
n_informative=1,
seed=2,
)
Z_X = np.hstack((Z, X))
Z_X_y = np.hstack((Z_X, y.reshape(-1, 1)))
Z_X_y = pd.DataFrame(Z_X_y, columns=["Z", "X", "y"])
Z_X_y = Z_X_y.replace({"y": 0.0}, "Class Zero")
Z_X_y = Z_X_y.replace({"y": 1.0}, "Class One")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
fig.tight_layout()
ax.tick_params(labelsize=15)
sns.scatterplot(data=Z_X_y, x="Z", y="X", hue="y", palette=PALETTE[:2][::-1], alpha=0.2)
sns.kdeplot(data=Z_X_y, x="Z", y="X", hue="y", palette=PALETTE[:2][::-1], alpha=0.6)
ax.set_ylabel("Variable Two", fontsize=15)
ax.set_xlabel("Variable One", fontsize=15)
plt.legend(frameon=False, fontsize=15)
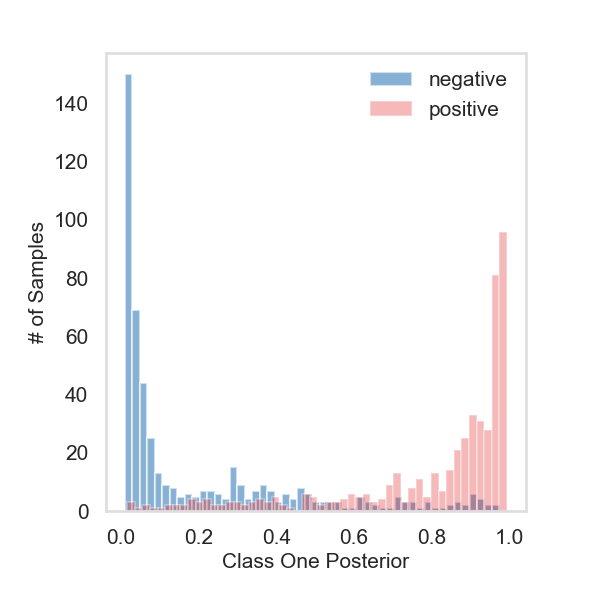
Fit the model with X and Z#
# initialize the forest with 100 trees
est = HonestForestClassifier(
n_estimators=100,
max_samples=1.6,
max_features=0.3,
bootstrap=True,
stratify=True,
tree_estimator=MultiViewDecisionTreeClassifier(),
random_state=1,
)
# fit the model and obtain the tree posteriors
_, observe_proba = build_oob_forest(est, Z_X, y)
# generate forest posteriors for the two classes
observe_proba = np.nanmean(observe_proba, axis=0)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
fig.tight_layout()
ax.tick_params(labelsize=15)
# histogram plot the posterior probabilities for class one
ax.hist(observe_proba[:500][:, 1], bins=50, alpha=0.6, color=PALETTE[1], label="negative")
ax.hist(observe_proba[500:][:, 1], bins=50, alpha=0.3, color=PALETTE[0], label="positive")
ax.set_ylabel("# of Samples", fontsize=15)
ax.set_xlabel("Class One Posterior", fontsize=15)
plt.legend(frameon=False, fontsize=15)
plt.show()
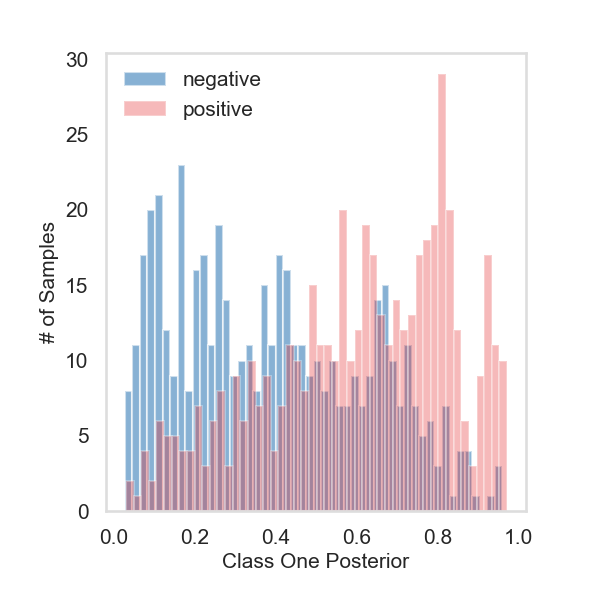
Fit the model with Z only#
# initialize the forest with 100 trees
est = HonestForestClassifier(
n_estimators=100,
max_samples=1.6,
max_features=0.3,
bootstrap=True,
stratify=True,
random_state=1,
)
# fit the model and obtain the tree posteriors
_, single_proba = build_oob_forest(est, Z, y)
# generate forest posteriors for the two classes
single_proba = np.nanmean(single_proba, axis=0)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
fig.tight_layout()
ax.tick_params(labelsize=15)
# histogram plot the posterior probabilities for class one
ax.hist(single_proba[:500][:, 1], bins=50, alpha=0.6, color=PALETTE[1], label="negative")
ax.hist(single_proba[500:][:, 1], bins=50, alpha=0.3, color=PALETTE[0], label="positive")
ax.set_ylabel("# of Samples", fontsize=15)
ax.set_xlabel("Class One Posterior", fontsize=15)
plt.legend(frameon=False, fontsize=15)
plt.show()
Calculate the statistic#
def Calculate_MI(y_true, y_pred_proba):
# calculate the conditional entropy
H_YX = np.mean(entropy(y_pred_proba, base=np.exp(1), axis=1))
# empirical count of each class (n_classes)
_, counts = np.unique(y_true, return_counts=True)
# calculate the entropy of labels
H_Y = entropy(counts, base=np.exp(1))
return H_Y - H_YX
joint_mi = Calculate_MI(y, observe_proba)
mi = Calculate_MI(y, single_proba)
print("CMI =", round(joint_mi - mi, 2))
CMI = 0.23
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.842 seconds)