ilastik¶
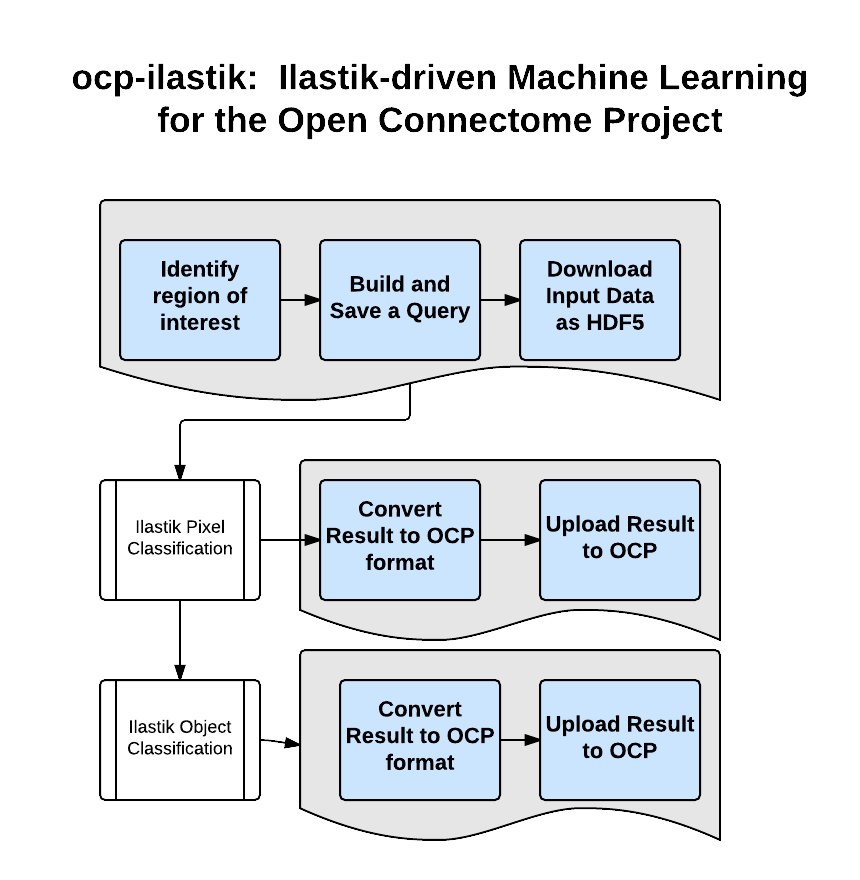
ilastik is a tool developed to do machine annotation and is widely used by the connectomics community. We present a lightweight protocol and data exchange format to allow users to use ilastik and OCP together. This provides an easy method for users to quickly prototype, build, and deploy machine learning solutions to neuroscience problems. The figure below outlines a sample workflow. The initial version of this workflow supports both pixel classification and an object detection step.
The example classifiers presented are used as a capability demonstration, not to demonstrate outstanding classification performance. If you would like to contribute a better performing classifier, please contact us.
Ilastik already supports exchanging data in hdf5 format. The wrappers and functions provided here are used to help read in raw OCP data and format the classifier output into RAMON objects suitable for uploading to OCP project databases.
We currently have a bug when running ilastik object detection in headless mode. We expect to resolve this before 8/31/2015.
LONI modules and an example workflow exist to enable rapid development.
Pixel Classification Train¶
- Identify a region of interest in OCP, and note the data server, token, resolution, and coordinates
- Create a query, using the instructions for OCP RESTful queries, CAJAL, or OCPy (CAJAL: cubeCutoutPreprocessAdvanced.m).
- Download a raw data volume in HDF5 format (CAJAL: cubeCutout.m)
- Using ilastik, build a pixel classifier, following the Pixel Classification instructions in Ilastik
- Save your ilastik project, containing your trained classifier
Pixel Classification Deploy¶
- Identify a region of interest in OCP, and note the data server, token, resolution, and coordinates
- Create a query, using the instructions for OCP RESTful queries, CAJAL, or OCPy (CAJAL: cubeCutoutPreprocessAdvanced.m).
- Download a raw data volume in HDF5 format (CAJAL: cubeCutout.m)
- Classify the volume of interest using Ilastik in headless mode.
- Reformat (using ilastikPixelToRAMON.m) and upload results (using CAJAL: cubeUploadProbabilities.m)
Ilastik Command:
<ilastik executable> --headless
--project <project file>.ilp
--output_format hdf5
--output_filename_format <output filename>
<path and filename for raw data>/<hdf5 dataset>
Object Detection Train¶
- Identify a region of interest in OCP, and note the data server, token, resolution, and coordinates
- Create a query, using the instructions for OCP RESTful queries, CAJAL, or OCPy (CAJAL: cubeCutoutPreprocessAdvanced.m).
- Download a raw data volume in HDF5 format (CAJAL: cubeCutout.m).
- Using ilastik, your raw data, and the results from a previous pixel classification step, build an object classifier, following the Object Classification Workflow
Object Detection Deploy¶
- Identify a region of interest in OCP, and note the data server, token, resolution, and coordinates
- Create a query, using the instructions for OCP RESTful queries, CAJAL, or OCPy.
- Download a raw data volume in HDF5 format
- Create pixel classification outputs using the corresponding ilastik classifier
- Pass pixel classification and raw data inputs into the ilastik object classifier
- Reformat (using ilastikObjectToRAMON.m) and upload results (using CAJAL: cubeUploadDense.m)
Ilastik Command:
<ilastik executable> --headless
--project=<projectfile>.ilp
--export_object_prediction_img
--raw_data <path and filename for raw data>/</hdf5 dataset>
--prediction_maps <path and filename for probability maps>.h5/<hdf5 dataset>
--output_filename_format <output filename>
--output_format hdf5
Example¶
“I want to add annotations to my dataset.”
This example walks obtaining data from OCP, building classifiers in ilastik and deploying these classifiers in the OCP framework. The definitive documentation is at ilastik.org. Here we seek to build a lightweight classifier to detect mitochondria in our images.
For pixel classification in ilastik
1. Get datasets for training and test. These volumes may be obtained via RESTful interface. One simple option is to copy and paste the following URLs into a web browser. All volumes should be renamed with an ‘.h5’ extension.
Pixel Classification Training Volume
http://openconnecto.me/ocp/ca/kasthuri11cc/hdf5/1/3000,4000/5000,6000/1000,1016/
Link to first slice
http://openconnecto.me/ocp/ca/kasthuri11cc/xy/1/3000,4000/5000,6000/1000/
Pixel Classification Test Volume / Object Detection Training Volume
http://openconnecto.me/ocp/ca/kasthuri11cc/hdf5/1/3000,4000/5000,6000/1017,1032/
Link to first slice
http://openconnecto.me/ocp/ca/kasthuri11cc/xy/1/3000,4000/5000,6000/1017/
Object Detection Test Volume
http://openconnecto.me/ocp/ca/kasthuri11cc/hdf5/1/3000,4000/5000,6000/1033,1048/
Link to first slice
http://openconnecto.me/ocp/ca/kasthuri11cc/xy/1/3000,4000/5000,6000/1048/
- Open Ilastik
- Create New Project > Pixel Classification
- Add new data > separate image > <training volume>
- Still in the input data tab, right click on dataset description, edit properties -> change storage to save with classifier; change axes to -> zyx
- In the feature selection tab, choose some features appropriate to your task (we choose color, edge, and texture with a sigma of 1 for this example)
- In the training tab, add two labels, mitochondria and background. We assume that your target class is the first label, throughout this example Live prediction can help guide you, but requires quite a bit of memory, especially for large datasets.
- Save project and exit.
- Run the Ilastik classifier, following the example above
- Convert output data to an OCP compatible format (probability channel needs to be chosen, xy axes need to be switched, and data should be converted to a RAMONVolume) ilastik object detection requires the raw ilastik output
- Upload result to OCP, using (using CAJAL: cubeUploadProbabilities.m)
For object detection in ilastik (depends on pixel classification)
- Open Ilastik
- Create New Project > Object Classification with Inputs of Raw Data + Pixel Prediction Map
- Load data
- In the threshold and size filter tab, we chose only one threshold, with sigma values defaulted to 1. Threshold = 0.7, and size filter = 1000-1000000
- In the features tab, select all features
- Add labels of mitochondria and background (target/clutter)
- In the object classification tab, label detections as either target or clutter
- This is sufficient for classification, although subsequent ilastik steps may help improve classifier performance.
- Save project and exit ilastik.
- Run the Ilastik classifier, following the example above
- Convert output data to an OCP compatible format (xy axes need to be switched and array squeezed. Making unique objects is handled in the next step)
- Group objects by connected component and upload to OCP using (using CAJAL: cubeUploadDense.m)
Sample classifiers:
./data/ilastik_mito_pixelclassification.ilp
./data/ilastik_mito_objclassification.ilp
Sample results:
http:///ocp/overlay/0.4/test_ilastik_prob1/xy/1/7000,8000/8500,9500/1010/
Advanced Topics/Future Functionality¶
- When uploading annotations processed as many small cubes, often some sort of padding or stitching operation is required. These will differ slightly depending on use cases. Examples exist (e.g., i2g, vesicle) to use as a starting point
- When running in an SGE cluster environment, we suggest limiting threads to 1 and RAM to the value specified in LONI to allow ilastik lazy operations to co-exist smoothly with SGE. To do this, specify the following environment variables: LAZYFLOW_THREADS=1 LAZYFLOW_TOTAL_RAM_MB=8000 run_ilastik.sh –headless ...